Classification of data segments by intersection over union
The most fundamental classification problem in computer vision is the image classification itself, where the label and the main object is a given output of an image as it fails to recognize type of the objects out of its bounding box localization.
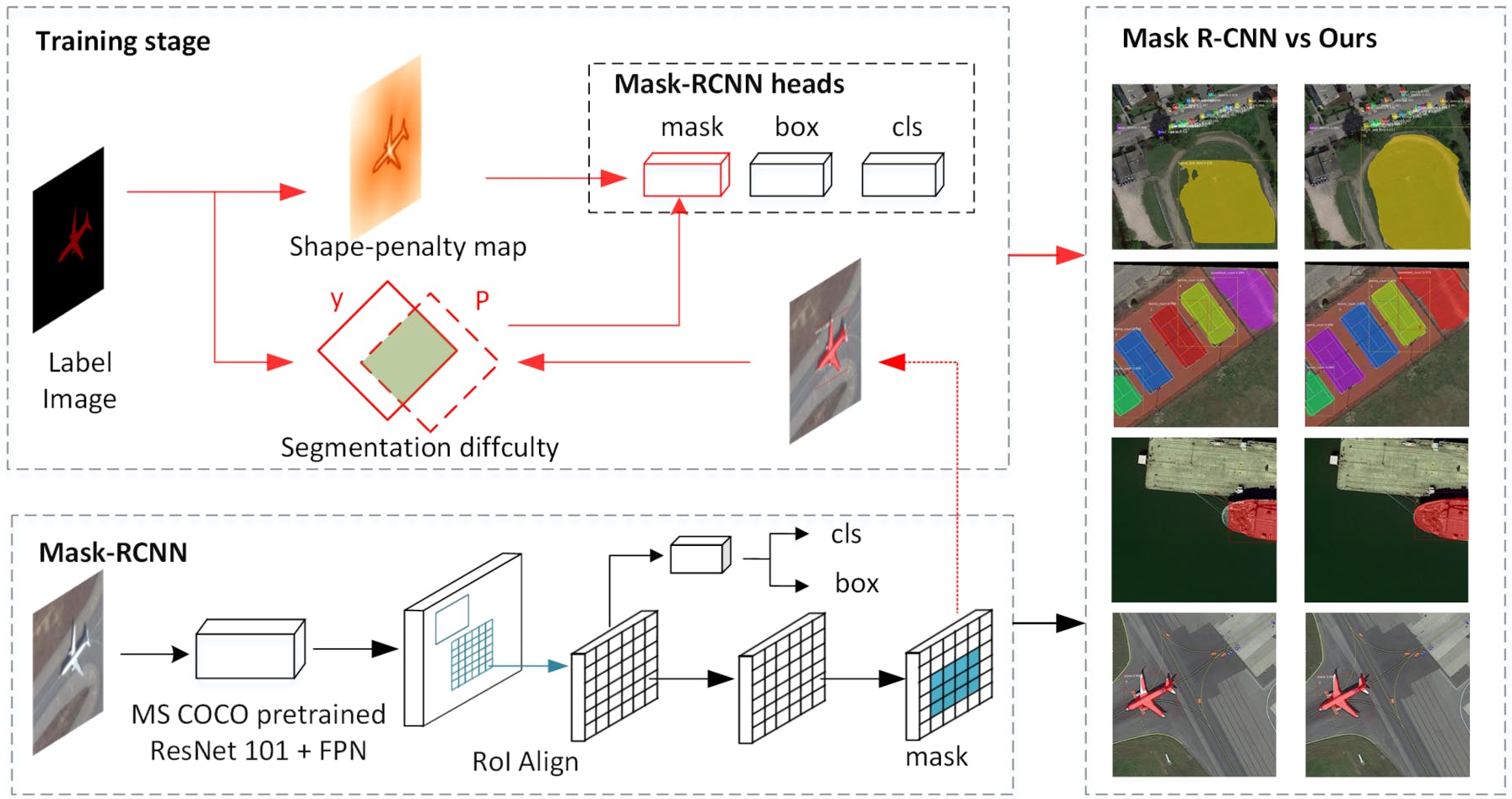
Accurate segmentation of instances remains difficult, especially at object edges. This problem is more prominent for instance segmentation in remote sensing imagery due to the diverse scales, variable illumination, smaller objects, and complex backgrounds. We find that most current instance segmentation networks do not consider the segmentation difficulty of different instances and different regions within the instance.
Classical convolution neural network architecture is typical with a certain size of input layer and output contraction and expansion paths. Convolutional response of an input is nothing more but multiplication where the dimensions might change of an output and is defined by each step of the convolutional layer and maximum pooling strided by a set number of shifts over the input matrix.
U-net architecture is designed for semantic segmentation and consists of two paths: encoding and decoding, contracting and an expansive path. Concatenation of the feature maps makes available localization details as the network propagates context information to the responding layer, therefore the expansive path is symmetric to the contracting part.
Standard U-net architecture can be extended into multi-class semantic segmentation with a controlled weight on supplied inputs. Segmentation model configuration and its backbone (as classification model without last dense layers of segmentation) is set by feature extraction technique, e.g. ResNet, Inception, MobileNet, EfficientNet used for magnetic resonance imaging, light microscopy, biomedical image segmentation.
Multiclass semantic segmentation can be done by structuring the data for the input in a number of classes, dividing image into patches, converting images and masks into tagged image files and compiled into a list of NumPy, not List, arrays. It also functions in the domain of linear algebra, fourier transform, and matrices. After converting the labels has to be encoded by a vectorizing array into a single vector, reshaped back and normalized.
The images must have tagged labels to generate masks in order to set classes for each segment and compile it with binary segmentation as the last layer has one output with probability reaching from zero or one.
Multiclass classification is characterized by categories as image size and number of classes, balancing the class weight for the dataset as defining a multi-unit model, this time using classification with categorical cross-entropy rather than binary. Intersection over a unit will get the argument that gives the highest probability from defined classes and find the class with maximum probability. The percentage can variate for the increased probability the weight must be increased for the class. Multiple encoders can be set to generate features for the input image, therefore it gives the highest accuracy and most advantage compared with other convolutional network models.
Tools:
Labeling tool for image masks www.apeer.com/annotate
ImageNet dataset with trained models https://www.image-net.org
Spyder open source light-weight IDE for Python https://www.spyder-ide.org
Keras or PyTorch python framework for artificial networks and deep learning, e.g. computer vision or natural language processing https://keras.io https://pytorch.org An example of hard instance learning and boundary shape analysis https://www.mdpi.com/2072-4292/14/1/23